G-force, or gravitational force, is a term commonly associated with physics, aerospace, and even amusement park rides. However, it plays a crucial role in fleet management and driving behavior analysis as well. By understanding g-force and its effects on driving, fleet managers can make significant strides in enhancing both safety and efficiency.
What is G-Force?
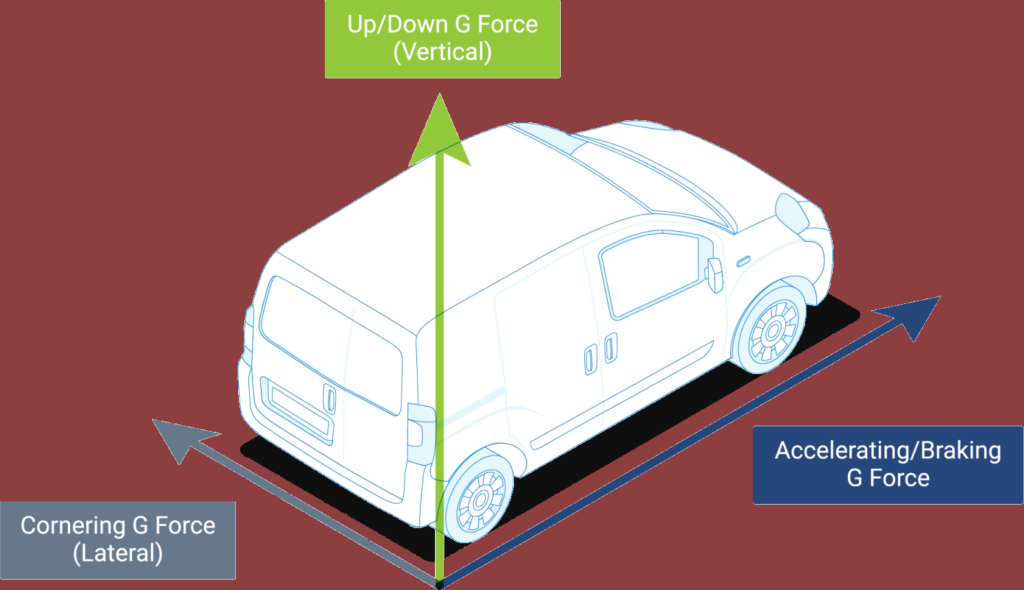
G-force, or gravitational force, is a measure of acceleration resulting from gravity or a similar force. It’s expressed as a multiple of the acceleration due to gravity (g), which is approximately 9.8 meters per second squared (m/s²). For instance, experiencing 2 g’s means you are subjected to an acceleration twice as strong as Earth’s gravity.
Relationship between G-Force and Acceleration
G-force in driving refers to the intensity of forces experienced when a vehicle changes speed or direction. Whether accelerating, braking, or cornering, drivers and passengers feel the effects of these forces. The quicker or more sudden the maneuver, the stronger the g-forces acting on the vehicle and its occupants.
What is harsh driving and how does G-force relate to it?
Harsh driving refers to aggressive maneuvers that expose a vehicle to significant g-forces, and it can be categorized into three main types:
- Harsh Acceleration: This occurs when a driver rapidly increases the vehicle’s speed, causing a sharp rise in forward g-forces. This behavior often signals aggressive driving and can lead to excessive vehicle wear and increased fuel consumption.
- Harsh Braking: This refers to sudden and forceful braking, resulting in high negative g-forces as the vehicle quickly decelerates. Such driving can be hazardous, increasing the likelihood of accidents and leading to greater brake wear and higher maintenance costs.
- Harsh Cornering: Taking turns at high speeds subjects the vehicle to strong lateral g-forces, which can compromise stability and control, raising the risk of rollovers or loss of traction.
Negative outcomes of harsh driving
Harsh driving not only heightens the risk of accidents but also directly affects vehicle health and operational costs. Here’s why:
- Safety Risks: Sudden and aggressive maneuvers generate high g-forces, which can lead to a loss of vehicle control, putting both the driver and others on the road at risk.
- Vehicle Wear and Tear: Essential components like brakes, tires, and suspension systems endure increased stress, resulting in more frequent and costly repairs or replacements.
- Fuel Efficiency: Rapid acceleration and abrupt braking are inefficient, leading to higher fuel consumption and escalating operational expenses.
- Driver Fatigue: Repeated exposure to intense g-forces contributes to driver fatigue, diminishing alertness and increasing the chance of errors on the road.
Monitoring and preventing Harsh Driving
Fleet management solutions, such as those from Kommnet Technologies, utilize advanced telematics systems to track driving behaviors. These systems employ accelerometers to detect and log instances of harsh acceleration, braking, and cornering. Through data analysis, fleet managers can:
- Identify drivers displaying aggressive driving patterns.
- Offer targeted training to foster safer driving habits.
- Implement incentive programs to reward smoother driving.
- Use real-time alerts to notify drivers of harsh maneuvers, encouraging immediate corrective action.
